Data formats
General
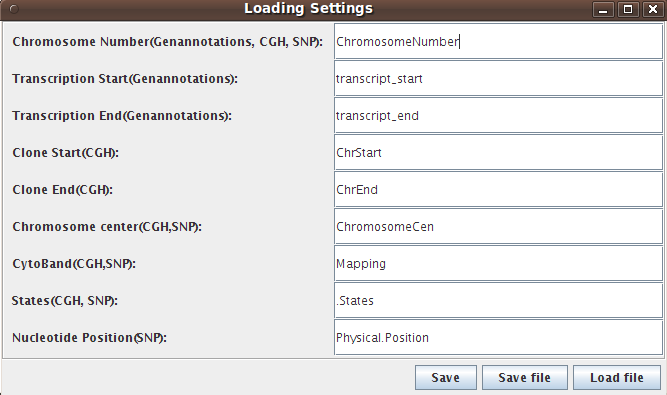
All data files have to be in tab delimited ascii format and missing values should be labeled "NA". Example files are available in the Download and Installation section. In the following we will describe the required data formats for the different data types. The names of the required columns can deviate from that in the description. In this case the user has to change the naming of the required columns in the "Loading Settings" menu.
File → Loading Settings
Gene expression data
SEURAT provides no preprocessing tools, gene expression data should be normalized and preprocessed beforehand. It is mandatory that the first column contains the gene IDs. The following columns should be named according to the sample IDs and contains the gene expression values of the respective samples.
Example:
geneID sample.1 sample.2 ... sample.n
gene.1 y.11 y.12 ... y.1n
gene.2 y.21 y.22 ... y.2n
...
gene.p y.p1 y.p2 ... y.pn
Clinical data
The first column should contain the sample IDs and these IDs should have the same format as in the gene expression file. Additional columns can contain any type of continous or categorical variable with the name of the variable in the first row.
Example:
sampleID variable.1 variable.2 ... variable.z
sample.1 x.11 x.12 ... x.1z
sample.2 x.21 x.22 ... x.2z
...
sample.n x.n1 x.n2 ... x.nz
Gene annotations
The first column has to contain the geneIDs and the gene names must be
the same as the gene names in the gene expression file. In case of
pathway informations where each gene can belong to different pathways,
the entries of pathway variables have to be lists of comma delimited
strings, e.g.: "cell_signaling, immunology, metastasis" or for
GO-terms: "molecular function|ATP binding|IEA|GO:0005524|GOA/IPI,
biological process|defense response to pathogen|IEA|GO:0042829|GOA/IPI,
cellular component|nucleus|IEA|GO:0005634" The name of a pathway
variable has to begin with "#" as the first character.
If the data set contains URLs (e.g. linking to cross-references like
PubMed),
the name of the respective column has to begin with a "@" symbol.
In order to associate the gene expression data with the array CGH data
the gene annotation file is needed. In addition the annotation file has
to have a column called "ChromosomeNumber" containing the number of the
chromosome and a column called "NucleotidePosition" containing the
starting position of the ORF of the gene. Additional
columns can contain any type of continuous or categorical variable with
the variable names in the first row.
Example:
geneID ChromosomeNumber NucleotidePosition #pathway annotation.1 ... annotation.v
gene.1 1 11223444 path1,path2 a.11 ... a.1v
gene.2 22 NA path1,path3 a.21 ... a.2v
...
gene.p X 1055 path5 a.p1 ... a.pv
Array CGH data
The array CGH data should have been normalized and preprocessed. A
segmentation algorithm should be applied to estimate cytogenetic gains
and losses. We used the R package
GLAD to preprocess our example data file.
The first column contains the cloneIDs of the CGH clones. To link the
states of the clones with the samples, a column with the name
"samplename.States" is needed for each sample. These columns contain
the result of the segmentation algorithm and the entries are "-1","0"
or "1", which correspond to a cytogenetic loss, no change or gain.
To link the CGH data with the gene expression data, the following six
columns are needed: "ChromosomeNumber", "ChrStart", "ChrEnd",
"ChromosomeCen", "Mapping". The variables "ChrStart" and
"ChrEnd" contain the start and end nucleotide positions of each CGH
clone. "Mapping" gives the cytoband
location of the CGH clone and "ChromosomeCen" gives the nucleotide
position of the centromere of the chromosome (so it is the same for all
clones on the same chromosome). See the example for details:
CloneID ChromosomeNumber ChrStart ChrEnd Mapping ChromosomeCen sample.1.States ... sample.n.States
clone.1 1 145 605 1q41 124300000 1 0
clone.2 22 11233 12034 22q13 11800000 -1 1
...
clone.w X NA NA Xq22 59500000 0 -1
SNP array data
Like the array CGH data also the SNP array data need to be preprocessed.
To normalize Affymetrix SNP chips (Genome-Wide Human SNP Arrays 6.0), we used the R package aroma.affymetrix.
A detailed R script descriping the preprocessing of Affymerix exon arrays (GeneChip Human Exon 1.0 ST Arrays) and SNP chips is available in the download section.
The first column of the snp file contains the SNPIDs. To link the states of the SNPs with the samples, a column with the name
"samplename.States" is needed for each sample. These columns contain
the result of the segmentation algorithm and the entries are "-1","0"
or "1", which correspond to a cytogenetic loss, no change or gain.
To link the SNP data with the gene expression data, the following
columns are needed: "ChromosomeNumber", "Physical.position",
"ChromosomeCen" and "Mapping".
SNPID ChromosomeNumber Physical.position Mapping ChromosomeCen sample.1.States ... sample.n.States
SNP.1 1 555 1q41 124300000 1 0
SNP.2 22 33030 22q13 11800000 -1 1
...
SNP.w X NA Xq22 59500000 0 -1